Maintaining weight within a healthy range is vital for optimal physical and mental well-being, but how do you find out that your weight is ideal according to your height? The simplest tool to measure weight is the Body Mass Index (BMI). Although BMI is not a perfect measuring metric, it is a widely used tool globally as a simple and easy screening method to determine and understand the risks associated with being overweight.
(To Shed Weight And Stay Healthy, Shop From Our Best Selling Fitness Supplements)
What Is BMI?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It is a number that tells you whether your weight is appropriate for your height. Unlike complex health check-ups, BMI does not need any special gadgets; it just needs your height and weight.
Even though BMI does not measure body fat percentage, it gives a fair idea of whether you are underweight, within a healthy range or overweight, which can identify your chances of developing lifestyle diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular problems.
Also Read: Obesity: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
How to Calculate BMI?
The formula to calculate BMI is very simple:
BMI = Weight ( in kg)/ Height (in m)2
Steps To Follow
Check your weight in kilograms.
Measure your height in meters and square height (height × height).
Divide your weight by the square height value.
Example: If you weigh 60 kg and your height is 1.60 m:
BMI = 60/ 1.6 ×1.6 =23.4
Your BMI is 23.4, which is considered healthy as per the Indian standard.
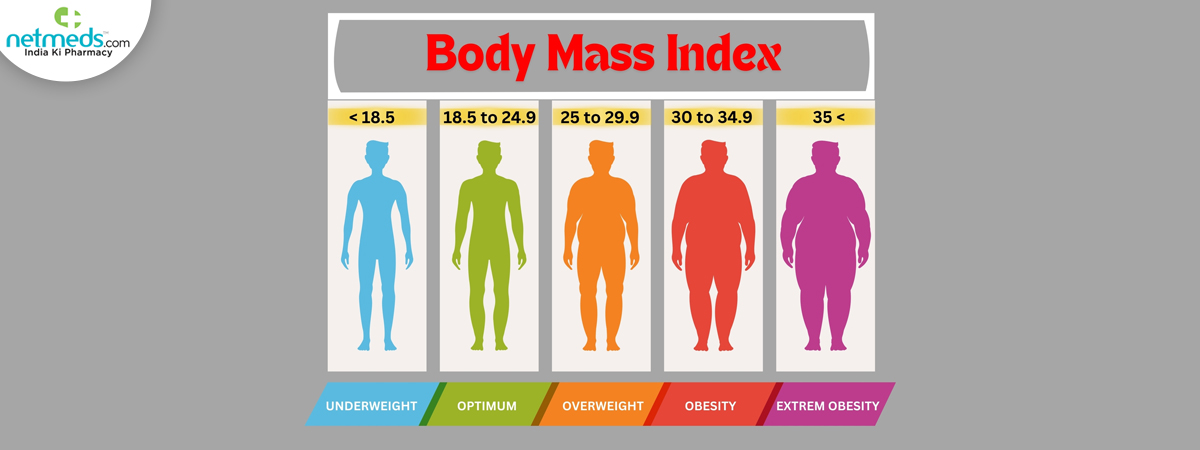
BMI Categories for Indians
Medical experts suggest that Indians need different BMI cut-offs compared to Western standards because we are at a higher risk of diabetes and heart disease at lower BMI values.
Here’s how BMI is classified for Indians:
BMI below 18.5 (Underweight)
Interpretation: Your weight is below the ideal weight for your height, which may indicate conditions like malnutrition, nutritional deficiencies or other health problems. In such cases healthcare provider may recommend person gain weight under proper medical guidance through healthy dietary practices and supplements to meet deficiencies.
BMI 18.5 – 24.9 (Normal Healthy)
Interpretation: Your weight is generally considered healthy for your height. The main goal here is to sustain this weight through a wholesome diet and regular exercise.
BMI 25 29.9 (Overweight At Risk)
Interpretation: Your weight is above a healthy range. Here, a moderate weight loss of 5-10% of current weight can significantly improve a person’s overall health markers and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
BMI 30-34.9 (Obese Class I)
Interpretation: You are at an increased risk for numerous obesity-related medical conditions. Gradual, sustained weight loss is highly recommended, combined with proper dietary management and medical guidance.
BMI 35 -39.9(Obese Class II, High Risk)
Interpretation: Your risk for obesity-related health conditions is very severe. A well-structured and tailored weight loss plan is often recommended comprising medical supervision and possibly more serious interventions, is required.
BMI 40.0 or higher (Class 3 - Severe Obesity)
Interpretation: This category carries the highest risk for serious health complications. A structured medical and nutritional therapy is needed to lose weight, which may include medication or bariatric surgery.
What Is the Importance Of BMI?
BMI serves as a quick and simple calculation to determine weight without any medical tests. It is an early warning that helps identify the risk of weight-related health problems.
BMI is used as a public health tool to monitor obesity and malnutrition trends in the population. Additionally, it is a personal tracker that aids you in checking obesity and malnutrition trends among the populace. Moreover, it is a personal tracking machine that helps you monitor your progress in your fitness journey.
How Can BMI Help Different People?
For individuals: It guides them to make healthy lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, and weight goals.
For doctors: It acts as a primary point to assess risks of diseases like diabetes or hypertension.
For policymakers: Helps to develop strategies and formulate nutrition and health programs.
Conclusion
BMI is a valuable health indicator and is one of the most accessible tools to personalise your weight loss plan. Additionally, it also allows you to set goals, track progress tracking and make informed decisions in your fitness journey. However, it does not distinguish between muscle and fat, nor does it measure fat distribution. That’s why medical professionals often pair it with other measurements like waist-to-hip ratio or body fat percentage.
(This article is reviewed by Kalyani, Chief Content Editor)
Author Profile:
M Sowmya Binu:
With over 15 years of expertise and a Postgraduate degree in Nutrition, M Sowmya Binu is a seasoned professional in the field of nutrition. Specialising in tailoring personalised diet plans, she underscores the significance of a balanced approach to health, emphasising the integration of medication with dietary intake for holistic wellness. Passionate about equipping individuals with knowledge to make informed decisions, Sowmya adeptly develops insightful content encompassing a wide array of topics, including food, nutrition, supplements, and overall health.
References:
https://www.japi.org/article/japi-73-4-11
Understanding Body Composition Analysis in Obesity Management
Khushboo Agarwal, Felix Manoharan, Nitin Kapoor
Body Mass Index
Obesity, BMI, and Health: A Critical Review
Frank Q Nuttall
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4890841/




.jpg)








